4 5 Series Alu Forging
4A11 and 4032 are Al-Si-Cu-Mg series Forged aluminium alloys. They are both forged and cast aluminium alloys. They can be strengthened by heat treatment. It has the advantages of small coefficient of thermal expansion and good wear resistance. It has good heat resistance, fatigue resistance and low temperature mechanical properties. It has good plasticity in hot state and good corrosion resistance.
4A11 and 4032 aluminium alloy forgings are mainly used to manufacture materials for piston and cylinder of steam engine, as well as complex forgings working below 200 C and bearing heavy loads.
For complex or heavy forgings, the water temperature during quenching can be increased to 65-80 â to avoid the deformation of forgings, but the mechanical properties will decrease.
Generally, the transfer speed during quenching should not exceed 10 s. For heavy forgings, the transfer speed should not exceed 15 s, so as to avoid affecting the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of the alloy.
The two alloys have good plasticity in hot state. They are suitable for extrusion into bar and various interface profiles, and for making various forgings.
5A02 alloy has low strength and high plasticity. Cold deformation can improve its strength, but it will reduce its plasticity. It has good properties of hydrogen atom welding, contact welding and friction stir welding. It can also be gas welding and has high corrosion resistance. In aircraft manufacturing, welding under moderate loads requires high process plasticity and corrosion resistance components, such as pipes, liquid containers and sliding frames, and also used to manufacture airplane mailboxes and conduits, welding wires, rivets and ship structures.
The melting temperature and casting temperature of 5A02 are 700-750 âand 690-730 â respectively. Alloy wires are used as solders and rivets. The machinability of 5A02O is not good, and it is improved under the condition of cold work hardening. The surface treatment process of 5A02 is similar to that of other aluminium alloys, but much worse than that of 6063 alloy.
The magnesium content of 5A05 alloy is high, although cold deformation can improve its strength, but the plasticity will decrease accordingly; the O state material has higher plasticity, and the H * 4 material has medium plasticity. Although the technological plasticity of 5A05 alloy is high, the cold work hardening speed is fast in the process of cold deformation, which should be paid attention to when processing parts.
In aircraft manufacturing, the alloy is usually used to manufacture parts with high process plasticity and corrosion resistance, as well as welded pipes, liquid containers, welded structural parts, aircraft skin skeleton and so on.
5A06 alloy has the highest Mg content (6.3%) and the highest Mn content (0.65%). The average total content of Mg and Mn reaches 7%. Because of its high strength, relatively low plasticity, good corrosion resistance and weldability, it can be processed into plates, tubes, rods, profiles, wires and forgings, die forgings, etc. It has been widely used in aviation, aerospace, missiles, ships, automobiles, tanks and other industries. Mainly used for welding structure, cold forging parts, stress parts of welding vessels, aircraft skin skeleton parts and rivets.
5083 alloy is not widely used in the manufacture of aerospace vehicles. European Airbus uses a certain amount of this alloy in the manufacture of aerospace vehicles. In addition, some foreign companies use 5083 alloy to manufacture cruise missiles. The 5083 forged aluminium parts are used in railway vehicles, special automobiles, tanks, petrochemical containers, ship inspection, power electronics industry, etc.
The thermoplasticity of 5083 aluminium alloy forgings is low, and the processing rate of several passes is not too high at the beginning, which is controlled at 3%-5%. In the middle stage of forging, the hot-working structure increases, but the core of ingot is still as-cast structure and there is no plastic deformation. At this time, the processing rate should be increased so that the forgings can cross the fragile zone as soon as possible and the processing rate should be controlled at 5%-15%. In the later stage of forging, in order to compensate for the heat loss of forging, the same is true. In order to ensure the final structure and properties of hot rolled products, 15%-35% pass processing rate can be adopted.
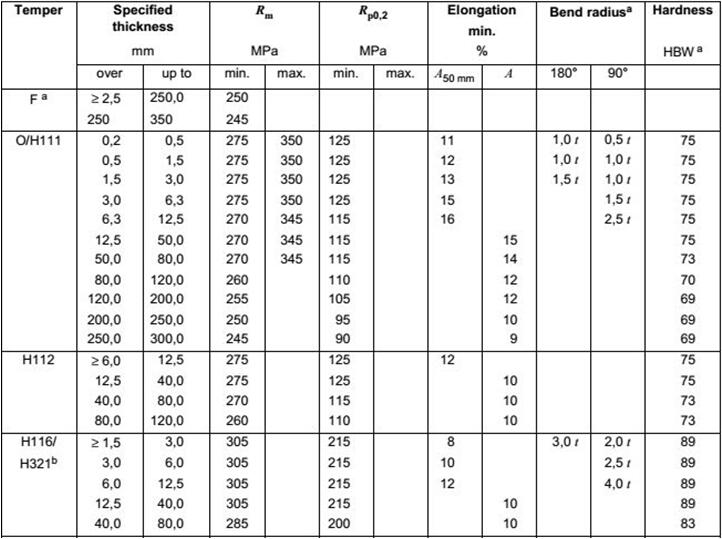
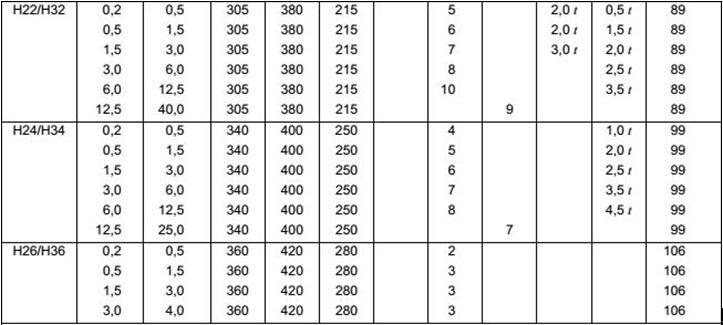
4A11 and 4032 aluminium alloy forgings are mainly used to manufacture materials for piston and cylinder of steam engine, as well as complex forgings working below 200 C and bearing heavy loads.
| Tensile Properties of 4A11 4032 Aluminum Alloy at Room Temperature and Low Temperature | ||||
| Temper | Temperature/â | Tension strength Rm/MPa | Prescribed plastic elongation strength Rp0.2/MPa |
Elongation A (%) |
| T62 | -200 | 460 | 337 | 11 |
| -100 | 415 | 325 | 10 | |
| T62 | -30 | 385 | 315 | 9 |
| 25 | 360 | 290 | 2.5 | |
For complex or heavy forgings, the water temperature during quenching can be increased to 65-80 â to avoid the deformation of forgings, but the mechanical properties will decrease.
Generally, the transfer speed during quenching should not exceed 10 s. For heavy forgings, the transfer speed should not exceed 15 s, so as to avoid affecting the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of the alloy.
The two alloys have good plasticity in hot state. They are suitable for extrusion into bar and various interface profiles, and for making various forgings.
| Type | Alloy | Projected areaï¼m2ï¼Or weightï¼kgï¼ | Temper | Standard |
| Free forgings | 5 series | ≤3000kg | OãF |
GBn223 ASTMB247 |
| 2ã6ã7 series | ≤3000kg | T6ãT4ãOãF | ||
| Mould forgings | 5 series | ≤2.5m2 | OãF | |
| 2ã6ã7 series | ≤2.5m2 | T6ãT4ãOãF |
5A02 alloy has low strength and high plasticity. Cold deformation can improve its strength, but it will reduce its plasticity. It has good properties of hydrogen atom welding, contact welding and friction stir welding. It can also be gas welding and has high corrosion resistance. In aircraft manufacturing, welding under moderate loads requires high process plasticity and corrosion resistance components, such as pipes, liquid containers and sliding frames, and also used to manufacture airplane mailboxes and conduits, welding wires, rivets and ship structures.
The melting temperature and casting temperature of 5A02 are 700-750 âand 690-730 â respectively. Alloy wires are used as solders and rivets. The machinability of 5A02O is not good, and it is improved under the condition of cold work hardening. The surface treatment process of 5A02 is similar to that of other aluminium alloys, but much worse than that of 6063 alloy.
The magnesium content of 5A05 alloy is high, although cold deformation can improve its strength, but the plasticity will decrease accordingly; the O state material has higher plasticity, and the H * 4 material has medium plasticity. Although the technological plasticity of 5A05 alloy is high, the cold work hardening speed is fast in the process of cold deformation, which should be paid attention to when processing parts.
In aircraft manufacturing, the alloy is usually used to manufacture parts with high process plasticity and corrosion resistance, as well as welded pipes, liquid containers, welded structural parts, aircraft skin skeleton and so on.
5A06 alloy has the highest Mg content (6.3%) and the highest Mn content (0.65%). The average total content of Mg and Mn reaches 7%. Because of its high strength, relatively low plasticity, good corrosion resistance and weldability, it can be processed into plates, tubes, rods, profiles, wires and forgings, die forgings, etc. It has been widely used in aviation, aerospace, missiles, ships, automobiles, tanks and other industries. Mainly used for welding structure, cold forging parts, stress parts of welding vessels, aircraft skin skeleton parts and rivets.
| 5A02 5A05 5A06 Chemical Composition | |||||||||||
| Alloy | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Zn | Ti | Others | Al | ||
| Each | Total | ||||||||||
| 5A02 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.15~0.40 | 2.0~2.8 | ï¼ | 0.6(Si+Fe) | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.15 | Rest |
| 5A05 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.30~0.6 | 4.8~5.5 | ï¼ | ï¼ | ï¼ | 0.05 | 0.15 | Rest |
| 5A06 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.50~0.8 | 5.8~6.8 | 0.2 | 0.0001~0.005 | 0.02~0.10 | 0.05 | 0.15 | Rest |
| Calibrated Mechanical Strength of 5A02 Alloy Semi-finished Products | |||||||
| Standard | Type | Temper | δ or d/mm | Tension strength Rm | A/% | ||
| Not less than | |||||||
| OD ≥50ï¼Wall thickness≤5.0 | ≥215 | ||||||
| GJB 2351 | Free forgingãDie forging | H112 | As agreement | ≥177 | ≥15 | ||
| HB 5204 | |||||||
|
GB/T 3196 GJB 2055 |
Wire | H×8 | 1.6~10.0 | ≥118 | ï¼ | ||
| Calibrated Mechanical Strength of 5A05 Alloy Semi-finished Products | |||||||
| Standard | Type | Temper | δor d/mm | Tension strength Rm/Mpa | Rp0.2/Mpa | A/% | |
|
GJB 2351 |
Free forgingãDie forging | H112 | As agreement |
≥196 ≥220 |
ï¼ ï¼ |
≥10 ≥12 |
|
| Calibrated Mechanical Strength of 5A06 Alloy Semi-finished Products | |||||||
| Standard | Type | Temper | δor d/mm | Tension strength Rm/Mpa | Rp0.2/Mpa | A/% | |
|
GJB 2351 |
Free forgingãDie forging | H112 | As agreement |
≥196 ≥220 |
ï¼ ï¼ |
≥10 ≥12 |
|
| Type | Alloy | Projected areaï¼m2ï¼Or weightï¼kgï¼ | Temper | Standard |
| Free forgings | 5 series | ≤3000kg | OãF |
GBn223 ASTMB247 |
| 2ã6ã7 series | ≤3000kg | T6ãT4ãOãF | ||
| Mould forgings | 5 series | ≤2.5m2 | OãF | |
| 2ã6ã7 series | ≤2.5m2 | T6ãT4ãOãF |
5083 alloy is not widely used in the manufacture of aerospace vehicles. European Airbus uses a certain amount of this alloy in the manufacture of aerospace vehicles. In addition, some foreign companies use 5083 alloy to manufacture cruise missiles. The 5083 forged aluminium parts are used in railway vehicles, special automobiles, tanks, petrochemical containers, ship inspection, power electronics industry, etc.
The thermoplasticity of 5083 aluminium alloy forgings is low, and the processing rate of several passes is not too high at the beginning, which is controlled at 3%-5%. In the middle stage of forging, the hot-working structure increases, but the core of ingot is still as-cast structure and there is no plastic deformation. At this time, the processing rate should be increased so that the forgings can cross the fragile zone as soon as possible and the processing rate should be controlled at 5%-15%. In the later stage of forging, in order to compensate for the heat loss of forging, the same is true. In order to ensure the final structure and properties of hot rolled products, 15%-35% pass processing rate can be adopted.
| Alloy | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Ni | Zn | Ti | Ga | Others | Alu | |
| Each | Toal | ||||||||||||
| 5083 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.1 | 0.4-1.0 | 4.0--4.9 | 0.05--0.25 | -- | 0.25 | 0.15 | -- | 0.05 | 0.15 | Remainder |


| Type | Alloy | Projected areaï¼m2ï¼Or weightï¼kgï¼ | Temper | Standard |
| Free forgings | 5 series | ≤3000kg | OãF |
GBn223 ASTMB247 |
| 2ã6ã7 series | ≤3000kg | T6ãT4ãOãF | ||
| Mould forgings | 5 series | ≤2.5m2 | OãF | |
| 2ã6ã7 series | ≤2.5m2 | T6ãT4ãOãF |